The crucial role of the One Health approach in combating antimicrobial resistance
Antimicrobial resistance is a significant threat to our health, and we can address the situation if we know all the factors that can play a role in its development and spread.
Embracing the One Health approach is essential in this effort, as it recognizes the interdependence between the human, animal and environmental dimensions.
The bacteria, along with other microbes and plants, produce a wide range of bioactive molecules, including also antibiotics.
These antibiotics serve not only as drugs against bacteria; fulfill crucial biological functions in various organisms. They are most likely involved in cell-cell signalling between bacteria and other organisms in the environment (fungi, plants, insects, livestock animals and even humans), indicating a complex interplay between different communities of living organisms.
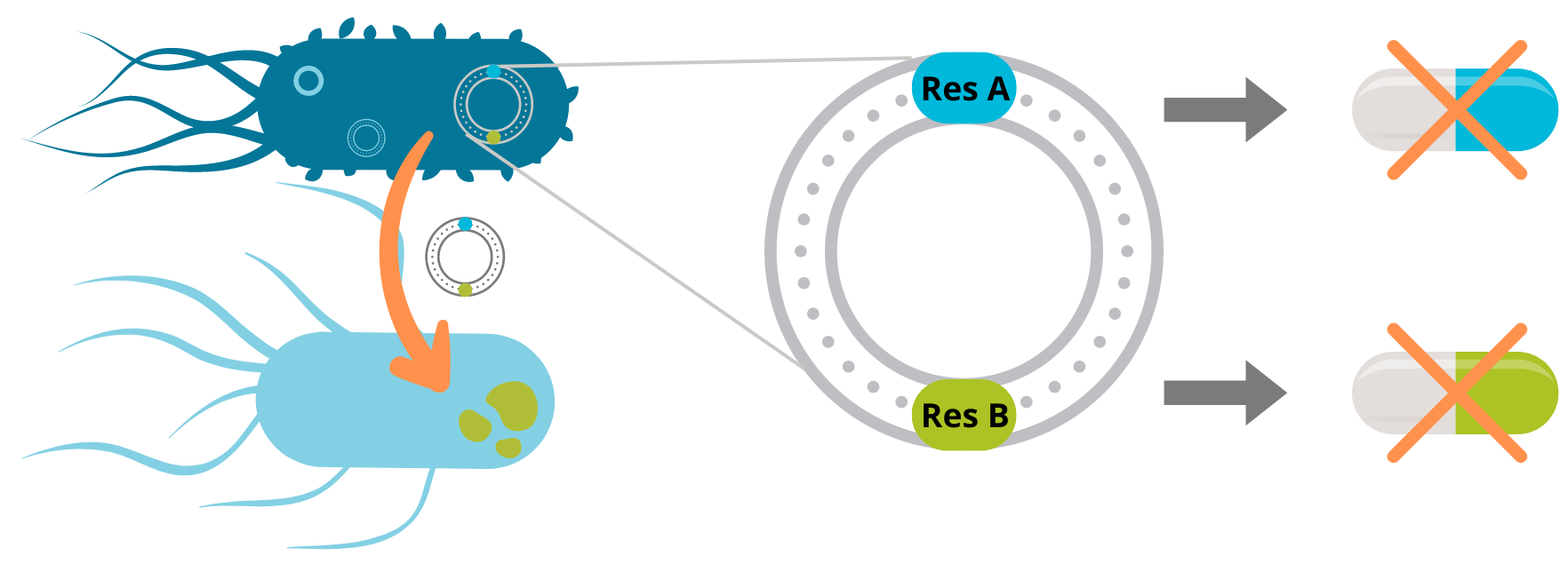
Moreover, the environmental microbiota serves as a huge reservoir of resistance genes, which can be transferred to pathogenic bacteria via cell-cell contacts. This gene exchange is a universal property of bacteria, the genetic material can jump between strains and species and spread very rapidly.
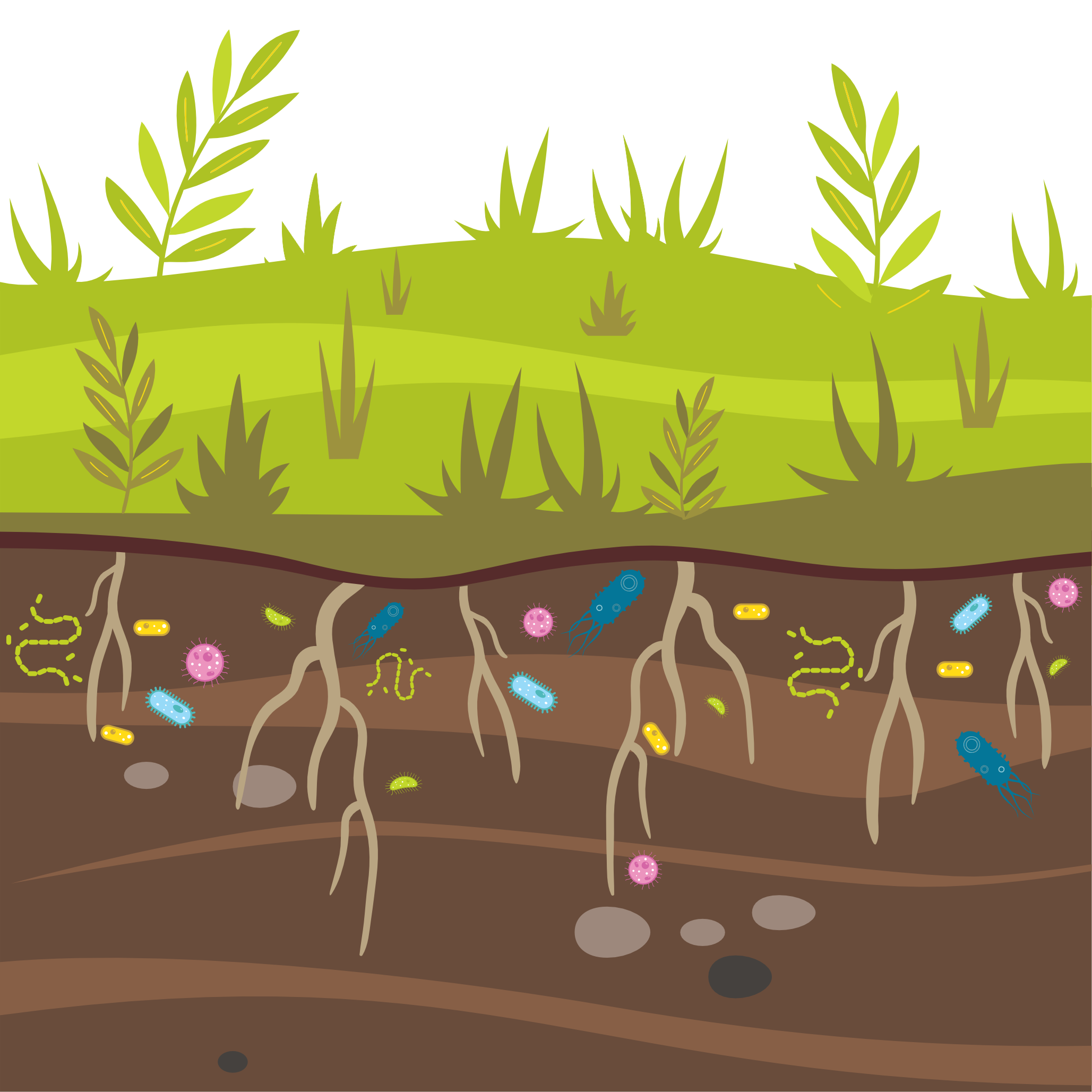
Recognizing that natural ecosystems, such as soil, which is one of the most species-rich habitats on earth, contain elements capable of developing antimicrobial resistance highlights the need for a holistic approach.
Human, animal, and environmental dimensions are intrinsically intertwined in the development and spread of antimicrobial resistance.


While it’s acknowledged that the development of antimicrobial resistance is a natural process, the proper use of antibiotics is pivotal in slowing its progression.
With concerted efforts and up-to-date knowledge, we can collectively work towards preserving the efficacy of antibiotics for generations to come.
Train yourself in AMR to help preserve the effectiveness of antibiotics for future generations
The AMR EDUCare project develops educational materials for healthcare professionals to reduce the spread of and exposure to antimicrobial resistance, focusing on optimizing antimicrobial prescribing and managing antimicrobial waste.
Subscribe to our newsletter to stay informed about course development and availability

Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the Health and Digital Executive Agency (HaDEA). Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.

